Production
The Tooling Production Process at Global Plastics
When a business needs particular plastic parts, components, or products, it will likely turn to an injection molding service provider such as Global Plastics for manufacturing what is needed. Before the piece in question can be produced, a quality, custom built mold must be created to withstand the rigors of repeated use in an injection molding machine. The tooling production process for making a mold involves a sequence of critical stages.
Machine Tooling for Manufacturing
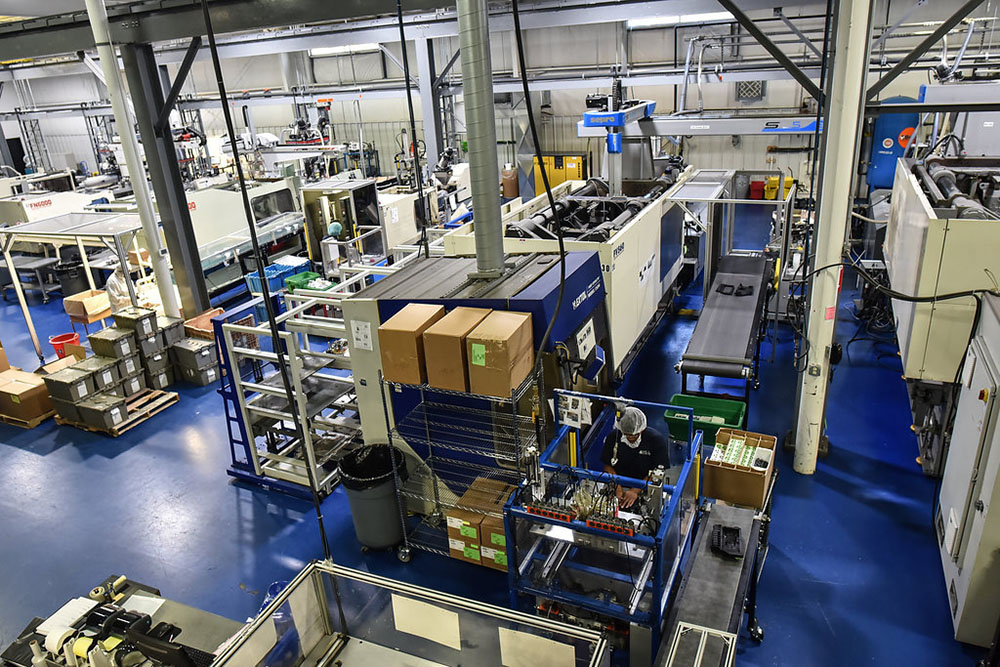
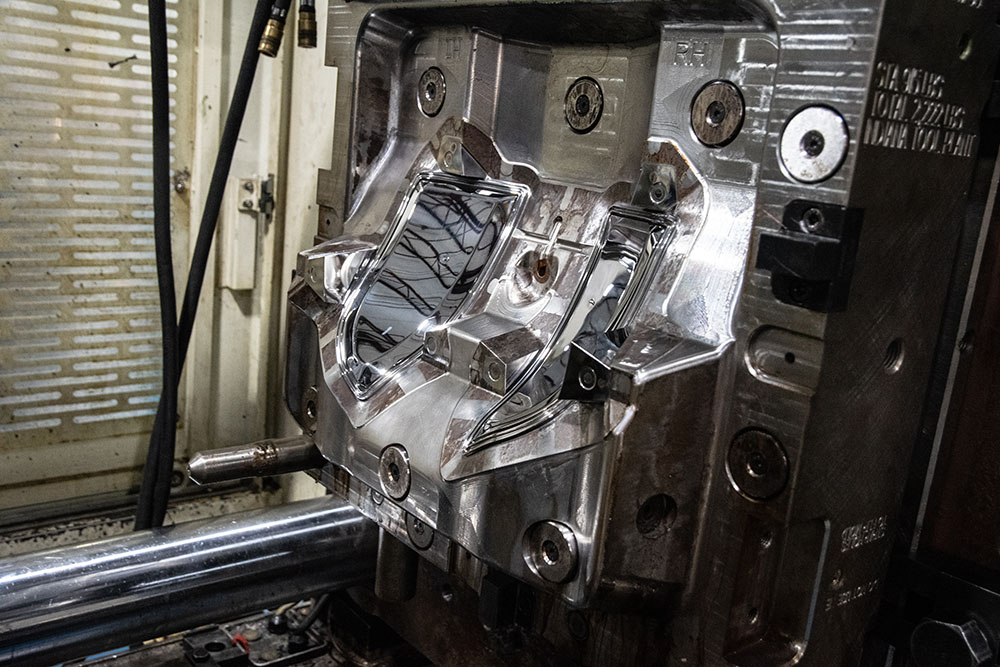

Everyone uses terminology in slightly different ways, but in the broadest sense, a definition for tooling or machine tooling is acquiring or making the manufacturing machines and components needed for production. The most common categories of tooling include jigs, fixtures, gauges, molds, dies, cutting equipment, and patterns:
- Jig: A custom-built tool that controls/guides another tool. When duplicating a key, for example, the original key is the jig that guides the key cutter to reproduce an accurate copy of the key. The jig allows the workpiece to move while the cutting tool remains stationary.
- Fixture: A tool that holds a workpiece stationary while the tool is moved to perform its action. It’s a secure mounting point for a workpiece.
- Gauge: Tools made to take measurements to gather dimensional data.
- Mold: A hollowed out block that can be filled with a liquid material that hardens into the desired shape. Most molds have two halves held together by an injection molding machine. When the injected material has cooled, the mold is opened and the part is ejected.
- Die: A custom tool to shape, cut, or form a material into a desired shape, such as a stamping die used with a press, a drawing die used to make wire, and casting dies used in molding.
- Cutting Equipment: Cutting tools used to remove material from a workpiece by shearing (saws, knives, cutting blades, etc.).
- Pattern: A replica of the object to be cast used to prepare the cavity into which molten material will be poured, such as a wooden pattern used to create the cavity in sand into which molten iron will be poured to create a cast-iron object using the sand casting process..
Because Global Plastics is an injection molding company, our tooling production is focused on molds. The word “mold” and “tool” are often used interchangeably in the industry because the mold is a tool used for injection molding. One of the benefits of working with us is that we have a full-service, in-house, professional tooling department with the expertise to create the mold used for an injection molding project.
Stages of Tooling Production to Make a Mold
An injection molding machine holds the pieces of the mold together with clamping pressure, heats the plastic pellets until they melt into liquid form, then injects the molten plastic into the cavity spaces of the mold under high pressure. When the molten plastic is sufficiently cooled and hardened, the mold can be opened to eject the plastic part, component, or product inside.
The channels through which the molten plastic flows into the mold cavity are called runners. Flow direction is controlled by a gate at the end of each runner. Precision design of the size and placement of gates and runners is needed to ensure even distribution of the plastic as well as efficiency of cycle times. Waterlines are also designed into the mold, which aids cooling and minimizes warping to ensure uniformity in the physical properties of the final plastic piece. Uneven cooling can result in “hot spots” or areas of weakness that reduce repeatability. Here are the stages of tooling production to make a mold:
- Feasibility: Engineers consider product specifications, what mold components are needed, the type of steel to be used for a large-volume production mold, and what plastic resin material is best suited to the desired plastic part, component, or product. These engineers are always on the lookout for potential problems or issues regarding part geometry or tolerance, as well as any special tooling features needed (lifters, slides, threads, etc.).
- Preliminary Design: A preliminary model is constructed to help determine mold size and steel size. This may include making a prototype mold in aluminum for test runs before making a production mold out of steel.
- Final Design: The tool builders receive the final mold design specifications and make any other needed adjustments for mold construction with careful monitoring of critical dimension requirements.
- Tool Construction: The mold is made by the tooling department and checked against a comprehensive checklist of design specifications and requirements.
- Production Use: The manufacturing department receives the tool (mold) and establishes the injection molding process parameters with full documentation. Initial production testing is undertaken to further refine any of the process parameters as needed. After customer validation of the plastic part, component, full production is launched.
Global Plastics: Your Tooling Production and Injection Molding Partner
The tooling production process at Global Plastics is aimed at creating a mold with high manufacturability that is easy to operate and maintain while lasting as long as possible to produce the plastic parts you need at the lowest possible cost. Because we have an in-house tooling department, this process goes much more smoothly than when you use two different providers, one for tooling production and another for injection molding production runs. Tooling a mold is a serious investment. Our expertise ensures you will see a solid return on investment as we optimize efficiency at every stage to minimize each expense to control the overall cost of making your mold. And we do it while also achieving superior quality in the final results. We invite you to get in touch with us through the contact us page of our website to learn more about how Global Plastics can meet your injection molding and tooling production needs.